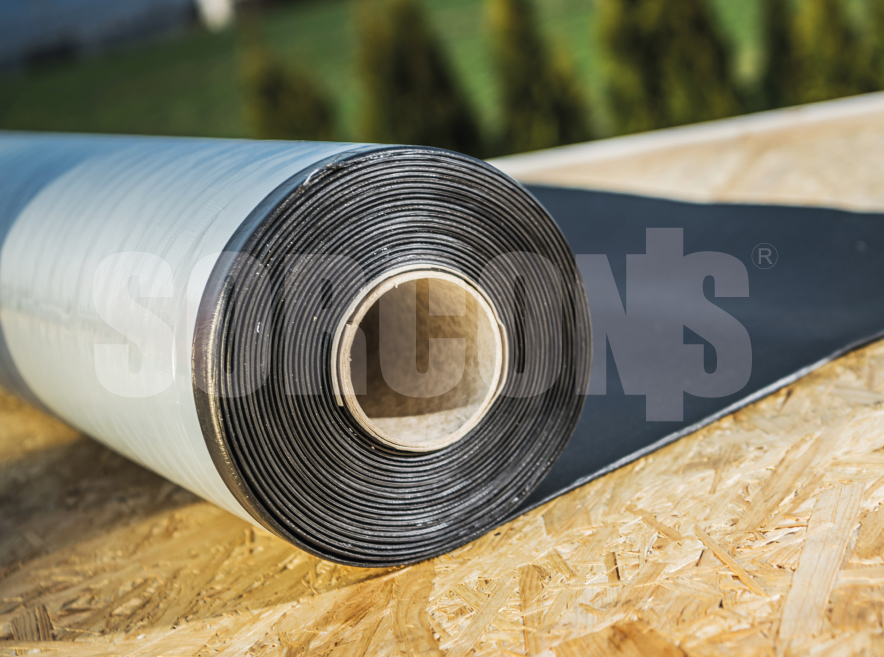
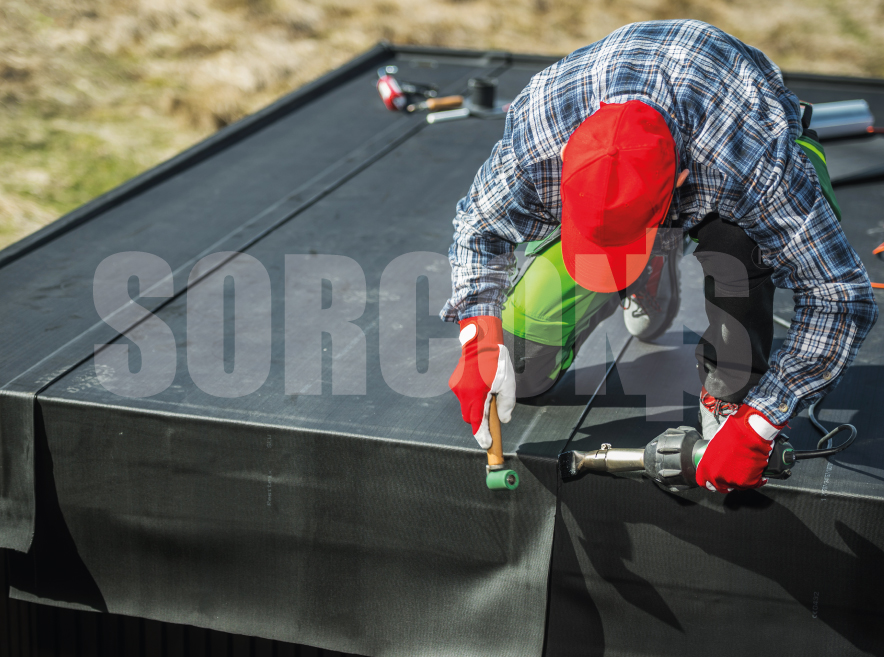
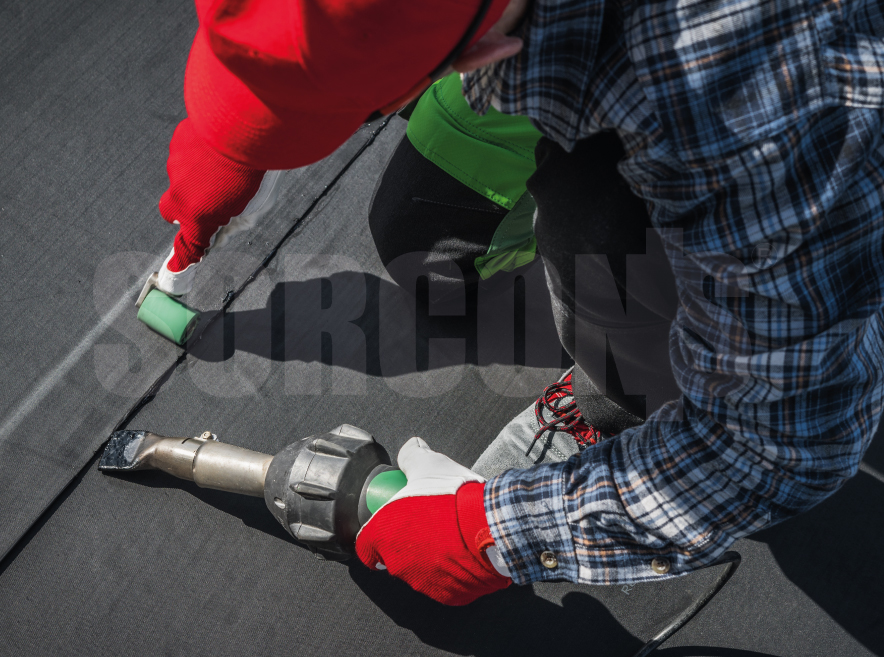
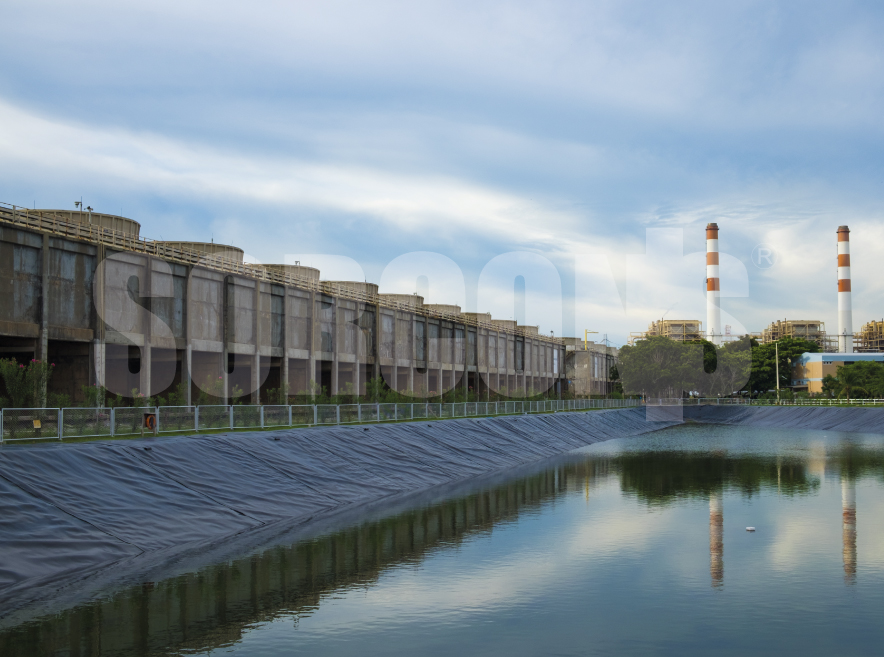
EPDM geomembrane is a synthetic rubber membrane commonly used in various applications, including EPDM membrane roofing system, containment, and environmental protection.
They are known for their high elongation at break, which allows them to stretch without tearing.
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer)
Excellent durability
Flexibility and elasticity
Chemical resistance
Root resistance
Ease of installation
Environmental sustainability
Versatile applications
Having excellent temperature resistance, with a typical service temperature range of -40°C (-40°F) to 120°C (248°F). EPDM Geomembrane allows them to withstand extreme hot and cold temperatures without degradation.
The best EPDM membrane exhibits excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and various organic compounds.
The versatility, durability, and waterproofing properties of the EPDM rubber membrane make it suitable for a wide range of applications requiring reliable containment and protection against water and contaminants.
Excellent durability
EPDM membrane roofing systems are known for their exceptional durability and longevity. They can withstand harsh environmental conditions, including UV radiation, extreme temperatures, and chemical exposure. EPDM geomembranes have a proven track record of performance in various applications, including landfill liners, pond liners, and water containment systems.
Flexibility and elasticity
With excellent EPDM membrane specifications, geomembranes have high flexibility and elasticity, allowing them to conform to irregular surfaces and accommodate ground movement without tearing or cracking. This flexibility makes them ideal for applications where settlement or shifting of the underlying soil is expected.
Chemical resistance
EPDM geomembranes exhibit excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and hydrocarbons. This resistance makes the EPDM geomembrane suitable for applications involving industrial wastewater containment, mining operations, and chemical storage facilities.
Root resistance
EPDM membrane thickness makes the surface inherently resistant to root penetration. This property makes them a popular choice for applications such as agricultural ponds, green roofs, and landscape water features, where root intrusion can cause damage to the geomembrane.
Ease of installation
EPDM geomembranes are relatively lightweight and flexible, making them easy to handle and install. EPDM membrane roofing materials can be easily seamed together using a variety of methods, including adhesive bonding, heat welding, or tape systems, allowing for efficient and secure installation.
Environmental sustainability
EPDM geomembranes are considered environmentally friendly as they are manufactured using a low-energy process and are free from toxic materials. EPDM geomembrane is also recyclable, reducing its impact on the environment.
Versatile applications
EPDM geomembranes find applications in a wide range of industries, including civil engineering, water management, agriculture, mining, and construction. EPDM geomembrane is used as liners for ponds, reservoirs, canals, landfill sites, secondary containment systems, and more.
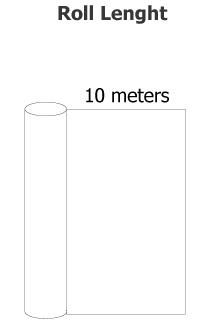
Roll Dimensions
HS Code 4002.70.00.00.00 |
|---|
Pond Liners
For ponds, lakes, and water features. They create a watertight barrier to prevent leakage and seepage, helping to retain water and maintain water levels.
Roofing Systems
For a durable and flexible waterproofing layer for flat or low-slope roofs, protecting the building from water intrusion.
Canal Linings
In canals and irrigation channels to prevent water seepage and ensure efficient water flow and distribution.
Mining Applications
In mining operations for various purposes, including lining tailings ponds, heap leach pads, and containment areas for storing chemicals and hazardous materials.
Agriculture
In agricultural applications, such as lining manure pits or creating water storage reservoirs, to prevent pollution and
water loss.
Environmental Protection
In environmental protection projects, such as lining contaminated soil sites or creating barriers for preventing pollution migration.
Aquaculture
In aquaculture systems, such as fish ponds or shrimp tanks, to maintain water levels and prevent seepage.
| Standard of Testing | Purpose of Testing | ||
TS EN 1850-2 | Visible defects | Tested | Passed |
TS EN 1848-2 | Lenght | Tested | Passed |
TS EN 1848-2 | Width | Tested | Passed |
TS EN 1849-2 | Thickness | Tested | Passed |
TS EN 1849-2 | Mass per unit area | Tested | Passed |
TS EN 1928 (METOD B) – EN 14150 | Water-tightness | Tested | Passed |
TS EN 12691 | Resistance to impact | Tested | Passed |
TS EN 1296TS EN 1928 (METOD B) | Resistance | Tested | Passed |
TS EN 1847TS EN 1928 (METOD B) | Resistance to chemicals | Tested | Passed |
TS EN 12310-1 | Tear resistance | Tested | Passed |
TS EN 12317-2 | Welded joint resistance | Tested | Passed |
TS EN 12730 (METOD B) | Resistance to staticloads | Tested | Passed |
TS EN 12311-2 | Tensile properties | Tested | Passed |
TS EN 12311-2 | Elongation at break | Tested | Passed |
EN ISO 527 | Tensile strength | Tested | Passed |
EN ISO 12236 | Resistance to static punching | Tested | Passed |
EN 12224 | Resistance to weather conditions | Tested | Passed |
EN 14575 | Resistance to oxidation | Tested | Passed |
ASTM D 1434 | Gas thightness | Tested | Passed |
TS EN 12317-2 | Resistance to peeling | Tested | Passed |
TS EN 1847 - TS EN 1928 | Resistance to alkalis | Tested | Passed |
TS EN 13501 | Combustion class | Tested | Passed |
TS EN 1931 | Water vapour permeability feature | Tested | Passed |